Are You or Someone You Care About Living with a Degenerative Cognitive Disease and Are You Well Prepared?
Mandate in Case of Incapacity
A mandate in case of incapacity is a document with legal value, which allows us to name in advance one or more individuals who will take care of our well-being and see to the administration of our assets in the event that we become unable to do so independently.
The person appointed for this role is a mandatary.
Consequently, when the mandatary seeks to homologate the mandate in case of incapacity, he will have to sign a mandate, previously notarized, either in minutes, or under private writing, or in the presence of two witnesses, before the individual in question is incapacitated.
Article 2166 from the Civil Code of Quebec enacts:
« A protection mandate is a mandate given by a person of full age in anticipation of his incapacity to take care of himself or to administer his property; it is made by notarial act en minute or in the presence of witness. The performance of the mandate is conditional upon the occurrence of the incapacity and homologation by the court upon application by the mandatary designated in the act. »
- Protection Mandate
It is possible that one may become unfit without first having a protection mandate homologated. The most common case is when a person has a degenerative cognitive disease and no longer has the necessary states of mind to take care of himself or herself or administer his or her property. When this happens, it is possible for anyone close to them, for example: father, mother, spouse, friend or relative, to apply to the court for the opening of a protection regime in their name[1]. Depending on the circumstances, it is also possible that the individual subject to the incapacity mandate may be assigned an advisor, tutor or curator to administer his or her property.
For more information, please visit our section about mandates in case of incapacity.
It is important to note that a protective mandate is not the same legal document as a will. While the mandate in case of incapacity creates legal effects when you are alive, the will does not take effect until the time of your death.
For more information regarding wills, please visit our section about Planning a Last Will and Testament.
- Homologation in Case of Incapacity
In certain circumstances, the law makes the effectiveness of certain legal acts subject to compliance monitoring by an authority, for example, a court. The judgment which confers authority to this act is called homologation[2].
- Steps for granting the protection mandate in case of incapacity
The factors to consider are based on three (3) evaluation criteria:
(1) The mandator’s ability to identify the potential danger in given situations,
(2) The ability of the mandator to express himself
(3) The mandator’s ability to assert his rights[3]
The mandatary will have to provide the court with:
- A medical report from an occupational therapist or doctor certifying the incapacity of the mandator; and
- A psychosocial report from a social worker certifying the incapacity of the mandatary[4].
When all of the above criteria are met, the mandatary will have to make an application to the court to have the incapacity mandate homologated. Usually, it constitutes what is called a motion to institute a proceeding in homologation of a mandate in case of incapacity and may be followed by a demand to establish a protective supervision.
Thereafter, the court’s intervener will interview the person appointed as mandatary to ensure that he or she is effectively able to meet the requirements of the mandate and has the required general skills [5].
The procedure for obtaining the granting of a homologation in case of incapacity:
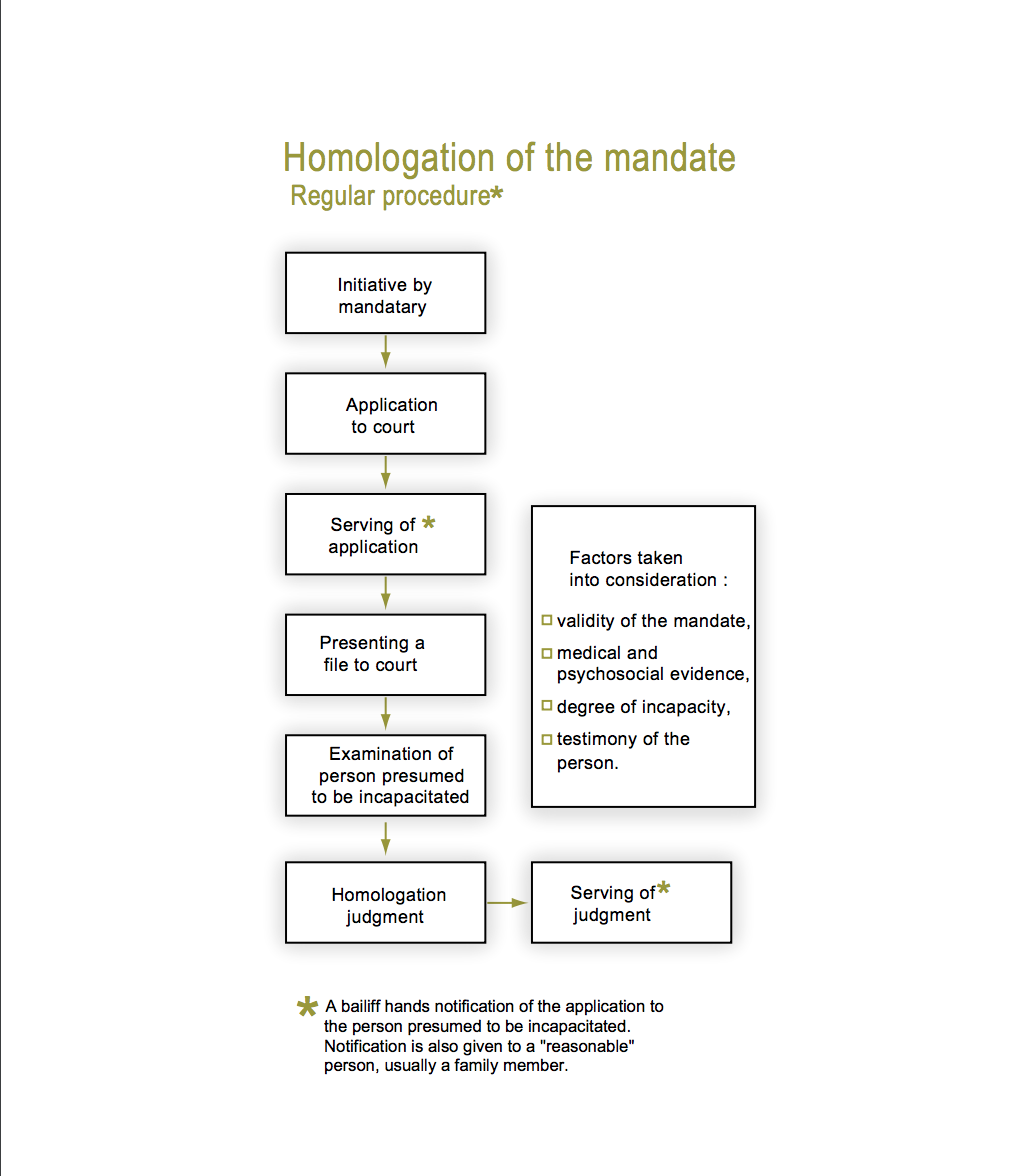
- Refusal of Granting the Mandate in Case of Incapacity
It should be noted that the court may refuse the homologation of a mandate in case of incapacity when the person claiming it acts in bad faith and/or against the interests of the mandator[6]. Indeed, « la présence de conflits familiaux est aussi un facteur dont doit tenir compte le juge dans sa prise de décision et peut constituer un motif sérieux de refuser l’homologation d’un mandat, au sens de l’article 2177 C.c.Q. »[7].
In short, the importance of having a mandate homologated is to verify the validity of the mandate, to verify the incapacity of the mandator, and if any, the degree of incapacity, and to verify the capacity of the mandatary, including the absence of conflicts of interest[8].
- Contesting the Homologation
An interested party may challenge the mandate in case of incapacity. However, this person will have to bear the burden of proof and demonstrate the incapacity of the mandator at the time of the drafting of the mandate.
The party contesting the power of attorney will have to prove that, at the time of the signing of the mandate of incapacity, as well as at the time of its drafting, the mandator was incapable of entering into a commitment with free and informed consent under C.C.Q., art. 1399. The mere fact that the mandator had partial and frivolous lucidity is insufficient for the recognition of capacity[9].
As for the burden of proof, it is reversed, and it is up to the person who alleges the mandator’s inability, to prove it[10]. This same evidence must be evaluated according to the balance of probabilities rule[11]. A simple doubt is not enough to reject the request and rebut the presumption of capacity[12].
Otherwise, if the capacity of the signatory of a mandate in case of incapacity is seriously questioned by a prima facie evidence, showing that the person was incapable at the time of the signing, the burden of proof then rests with the person claiming the validity of the act to prove the capacity of the signatory[13].
It is interesting to note that a person who contests the homologation of a mandate in the event of incapacity in good faith and without malice, may be reimbursed his judicial and extra-judicial fees from the assets of the person of full age unable to act in the event of the reversal of the homologation judgment[14].
- The Judgment
When all the criteria are met and satisfied and the court considers it appropriate to accept the mandate in case of incapacity, a positive judgment will be notified, confirming the homologation of the mandate in case of incapacity. Otherwise, the application will be rejected, and the mandate in case of incapacity will have no legal authority.
[1] C.C.Q., art. 268 et ss.
[2] Dictionnaire Juridique, 2019
[3] M.(L.) c. M.(J.), (C.S., 1996-03-08), SOQUIJ AZ-96021353, J.E. 96-971
[4] CAIJ, Volume 393 – La protection des personnes vulnérables (2015)
« L’évaluation clinique de l’inaptitude par les professionnels de la santé et des services sociaux : un défi comportant de nombreux enjeux ! ».
[5] M.V. et C.N., 2015 QCCS 2857, [17]
[6] T.A. c. L.B., 2012 QCCS 1642
[7] M.B. c. Me.L., 2014 QCCA 1271
[8] M.L. et D.T., 2017 QCCS 1758, [11]
[9] M.O. c. J.G., 2018 QCCS 1464
[10] M.D. (Re), 2015 QCCS 1152
[11] A.L. c. R.L., (C.S., 2005-06-30), SOQUIJ AZ-50321185, J.E. 2005-1453, [32]
[12] A.M. c. C.J., 2016 QCCS 3697
[13] A.L. c. R.L., (C.S., 2005-06-30), SOQUIJ AZ-50321185, J.E. 2005-1453, [32]
[14] A.M. c. C.J., 2016 QCCS 3697, [117] et ss.
If you are looking for a law firm with reasonable rates, quick and efficient turnaround time for your files and who provides personalized and effective follow-ups, call Schneider Attorneys at (514) 439-1322 ext. 112 or email us at client@schneiderlegal.com
The above noted text should not be construed as providing legal advice or a statement of your claim. The process highlighted above are merely parameters and barometers and do not constitute any warranties and guaranties with regards to your file at hand. We strongly recommend that you seek legal advice with a licensed attorney from the Barreau du Quebec or a notary at the Chambre des Notaires. Each case must be seen and analysed on its merits as the legal process may be complex and cumbersome.








